Replenishment System
The replenishment system automatically restocks inventory when levels fall below predefined thresholds. It supports both automated and manual workflows to maintain optimal stock levels across all locations.
System Architecture
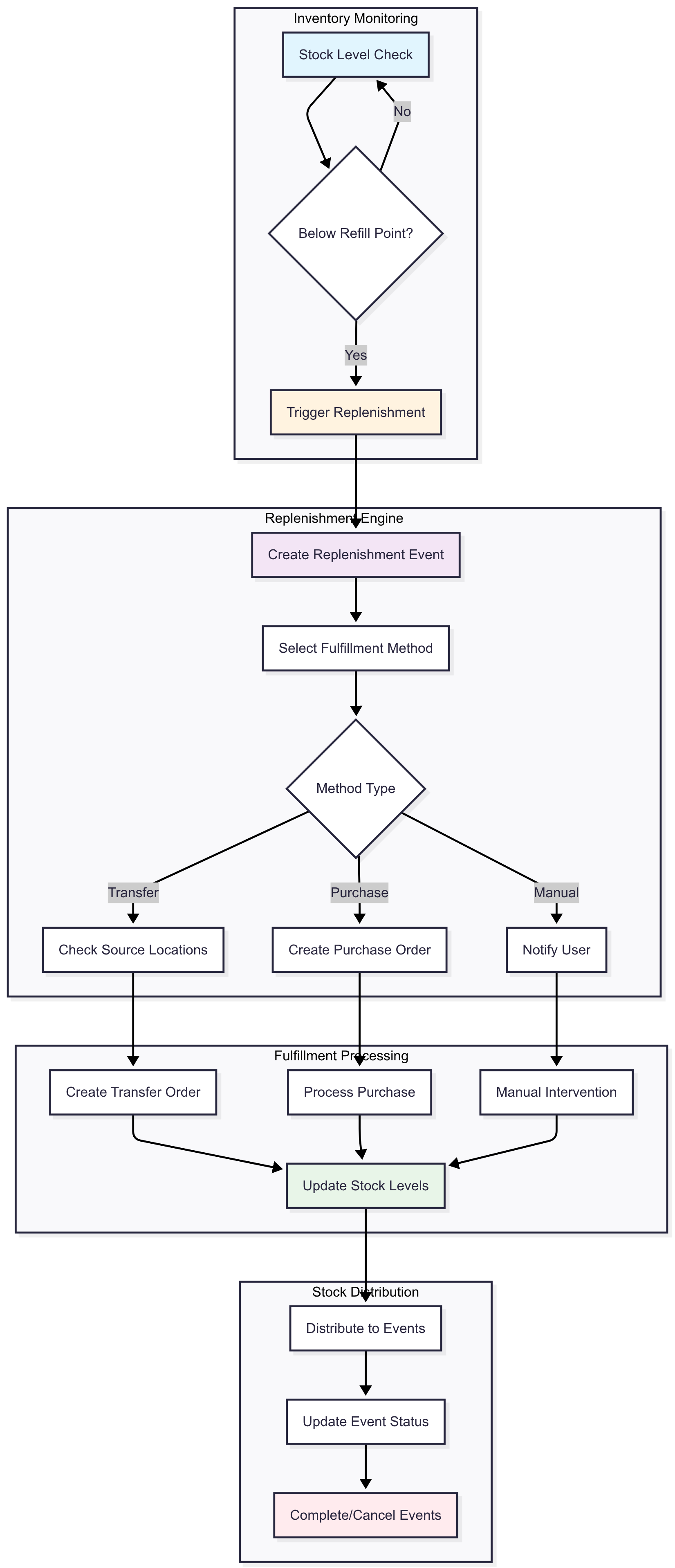
How Replenishment Works
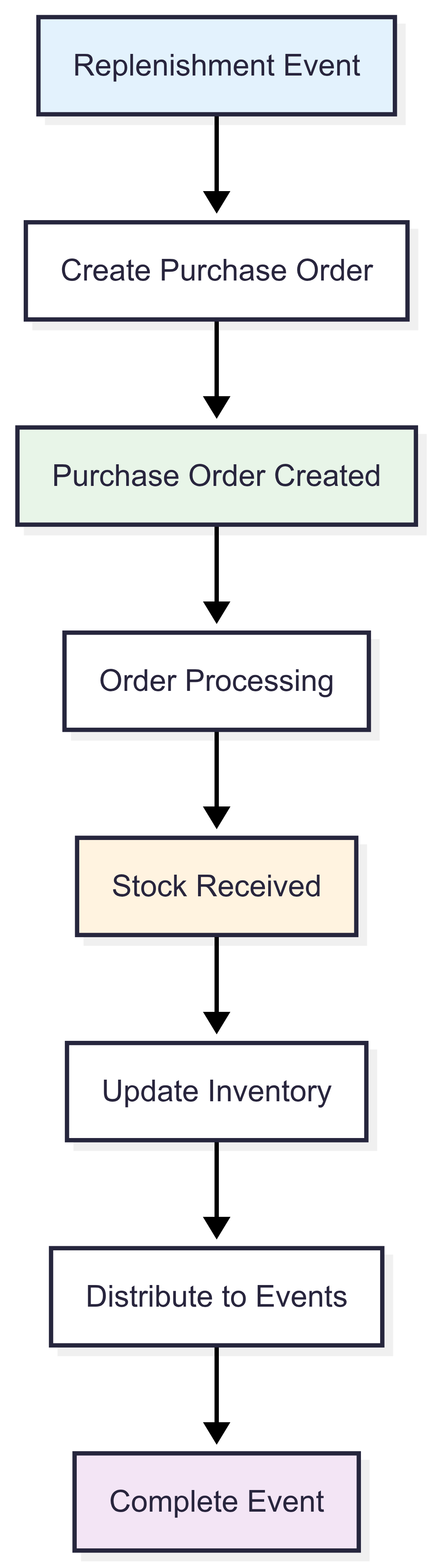
When inventory drops below a refill point, the system automatically:
- Creates a replenishment event
- Attempts fulfillment through configured methods (transfer or purchase)
- Updates inventory when stock arrives
Core Components
Refill Points
Define when to trigger replenishment:
- Refill Quantity: Minimum stock level that triggers replenishment
- Refill Methods: How to fulfill (transfer, purchase, manual)
- Priority: Order of preference for methods
Replenishment Events
Track restocking requests:
- Status: Pending, in progress, completed, or cancelled
- Quantities: Requested vs. fulfilled amounts
- Priority: Urgency level
Replenishment Fulfillments
Execute the actual restocking:
- Type: Transfer, purchase, or manual
- Status: Track progress through completion
- Reference: Link to orders or transfers
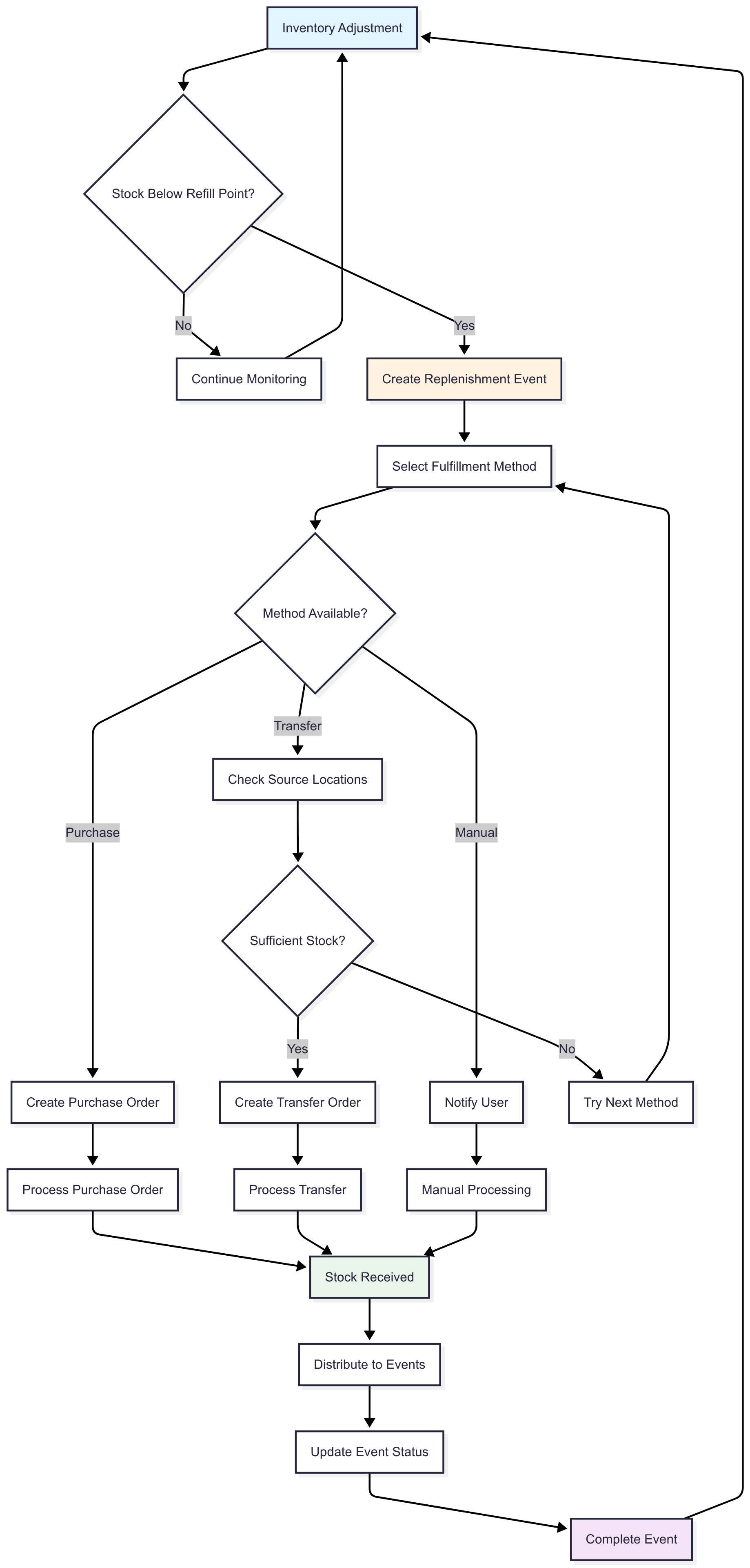
Automated Replenishment
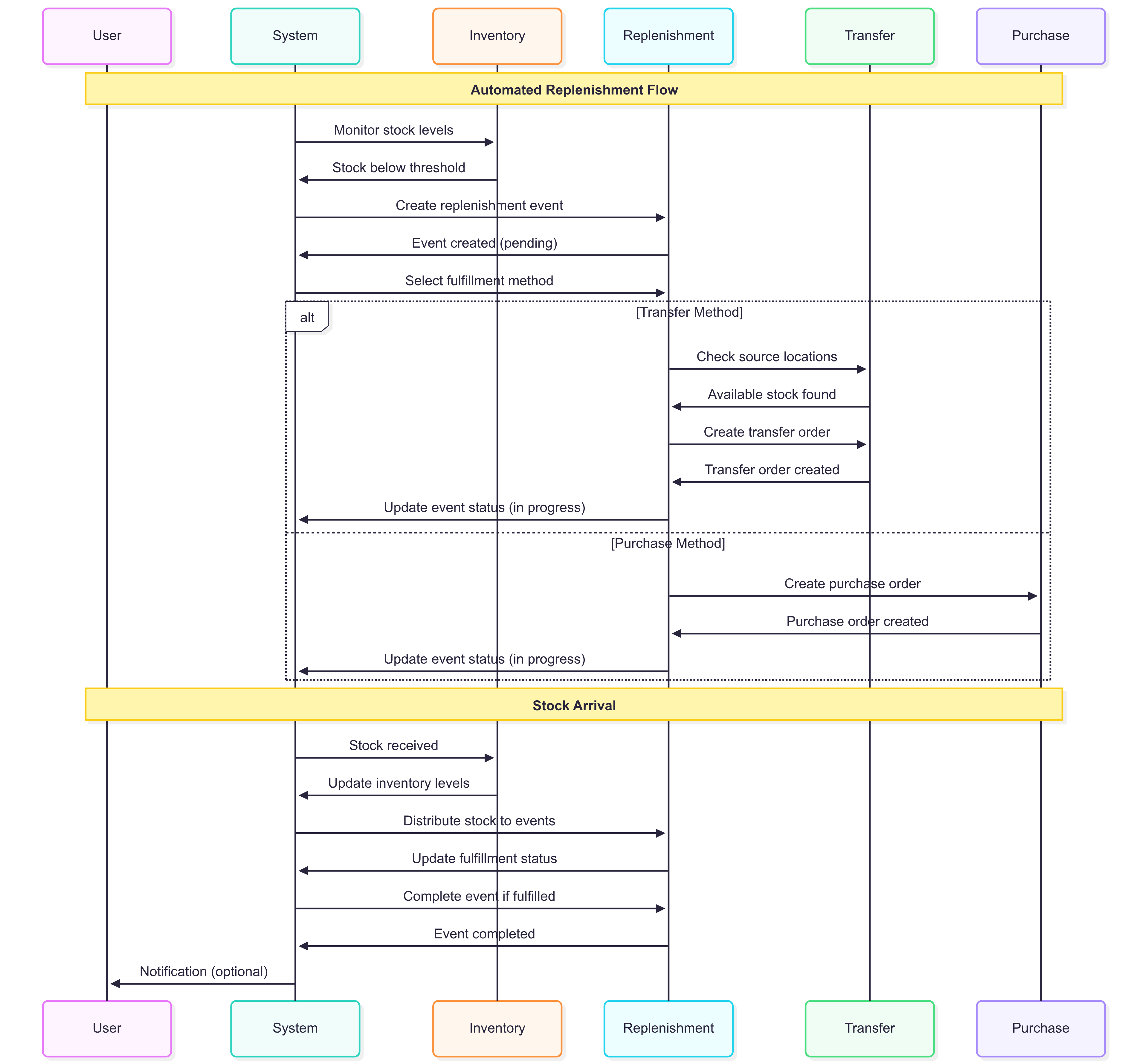
Process Flow
- Monitor: System continuously checks inventory levels
- Detect: Identifies when stock falls below refill point
- Create: Generates replenishment event automatically
- Fulfill: Attempts fulfillment via configured methods
- Distribute: Allocates incoming stock to pending events
Fulfillment Methods
- Transfer: Move stock from another location
- Purchase: Create a purchase order
- Manual: Require manual intervention
Manual Replenishment
You can create replenishment events manually when automated triggers don't meet your needs.
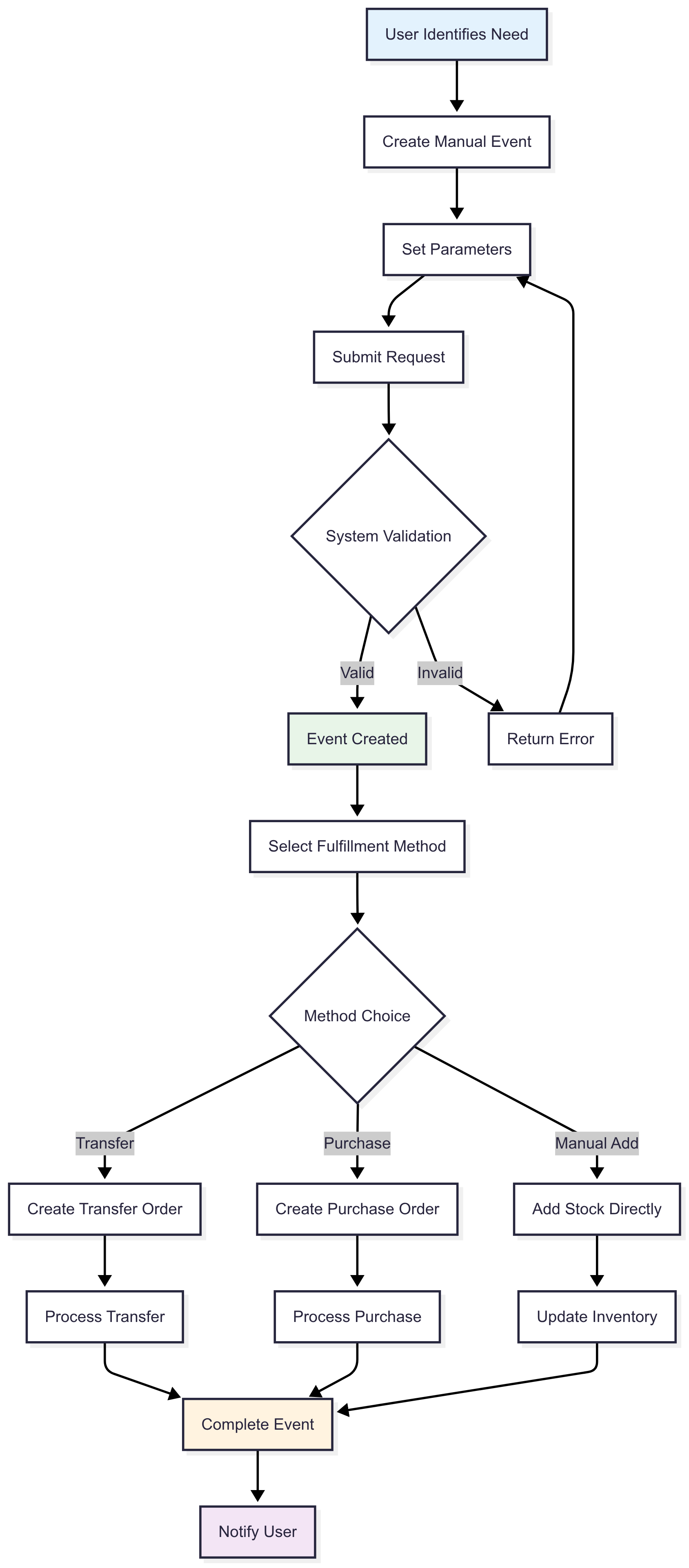
Transfer-Based Replenishment
When using transfers for replenishment:
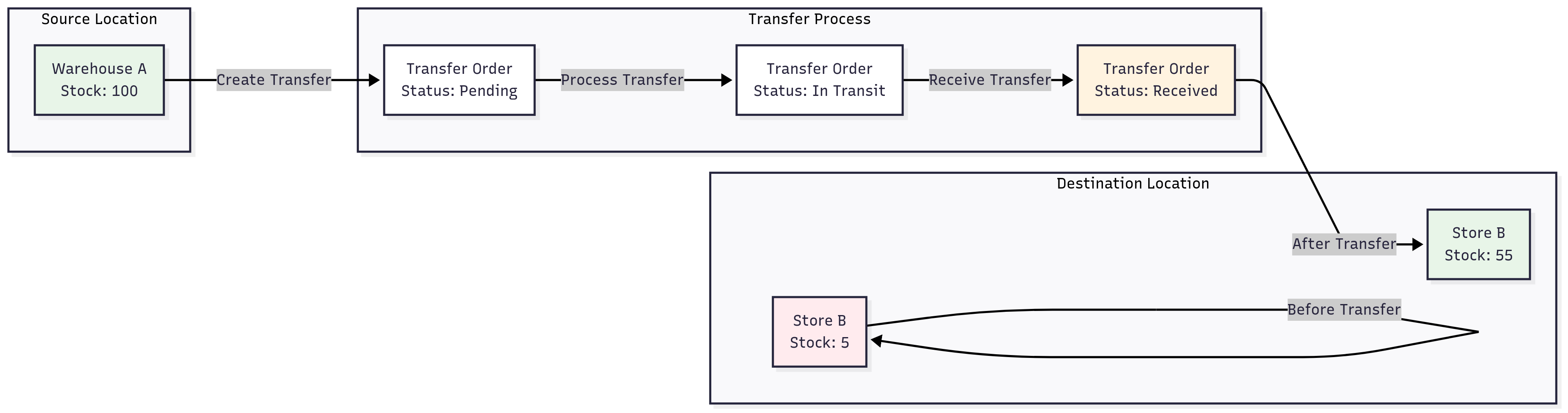
Transfer Process
- Validate: Check source location has sufficient stock
- Create: Generate transfer order
- Deduct: Remove stock from source
- Receive: Add stock to destination
Purchase-Based Replenishment
When stock isn't available for transfer, the system creates purchase orders:
Fulfillment Tracking
Track the progress of each replenishment fulfillment:
Fulfillment Status Progression
- Pending → Created, awaiting processing
- In Progress → Currently being processed
- Completed → Successfully fulfilled
- Failed → Could not be completed
Best Practices
Setting Up Replenishment
-
Calculate Refill Points based on:
- Historical usage patterns
- Lead times for fulfillment
- Safety stock requirements
-
Configure Multiple Methods:
- Set primary and backup fulfillment methods
- Define source location priorities
- Enable fallback options
-
Monitor Performance:
- Track completion rates
- Measure fulfillment times
- Review failed events regularly
Common Issues and Solutions
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
| Insufficient source stock | Configure multiple source locations |
| Failed transfers | Add retry logic and notifications |
| Delayed fulfillment | Set up escalation alerts |
| Incorrect quantities | Validate refill calculations regularly |
Key Metrics to Track
- Replenishment success rate
- Average time to fulfillment
- Stock-out incidents
- Manual intervention frequency
Related Documentation
- Inventory Management - Managing inventory levels
- Inventory Transfers - Moving inventory between locations
- Material Types - Reference for material types and configurations
- System Architecture
- How Replenishment Works
- Core Components
- Refill Points
- Replenishment Events
- Replenishment Fulfillments
- Automated Replenishment
- Process Flow
- Fulfillment Methods
- Manual Replenishment
- Transfer-Based Replenishment
- Transfer Process
- Purchase-Based Replenishment
- Fulfillment Tracking
- Fulfillment Status Progression
- Best Practices
- Setting Up Replenishment
- Common Issues and Solutions
- Key Metrics to Track
- Related Documentation